Laparoscopic Tubectomy Surgery in Guntur
What Is Laparoscopic Tubal Ligation?
Tubal ligation is viewed as a perpetual strategy for birth control. The fallopian tubes are cut or obstructed, which forestalls pregnancy by blocking the egg's way to the sperm and uterus. Laparoscopy makes it feasible to view and perform the procedure through tiny cuts in the mid-region.
For a laparoscopic tubal ligation, the specialist makes 2tiny cuts (entry points)— one in or just underneath the belly button (navel) and one lower on your mid-region. The abdominal cavity, where the reproductive organs are, is expanded with air or an innocuous gas so the specialist can see and try not to injure the abdominal organs or within the abdomen.
The surgeon places a shrill, lighted tube (laparoscope) through the entry point. The laparoscope has a lens that amplifies what the surgeon is seeing. The instrument that the specialist uses to trim (ligate) the tubes might be placed close by the laparoscope or through the cut simply over the pubic hair. The specialist glances through the laparoscope while moving this instrument to get the tubes cut in the right location.
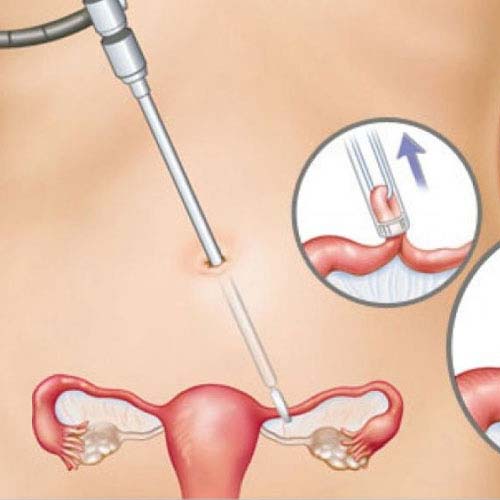
Laparoscopic tubal ligation leaves tiny scars. Laparoscopy is the ideal technique for a medical procedures for women who:
- Are healthy
- Are not overweight.
- Do not have anomalies of the pelvic organs, have never had a stomach or pelvic medical procedure, and have never had an infection of the pelvic organs like a pelvic inflammatory infection.
- Do not have endometriosis.
- Have not simply had a child
The hospital may send you guidelines on the most proficient method to prepare for your medical procedure, or an attendant may call you with directions before your medical procedure.
Just after a medical procedure, you will be taken to a recuperation region where attendants will focus on and notice you. In most cases, you will remain in the recuperation region for 1- 4 hours, and afterward, you will return home.